LwM2M vs MQTT: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Large-scale IoT deployments like smart water metering, smart farming, or smart city scenarios require multiple types of devices. These devices include IoT gateways, sensors, and meters, and they have the ability to share and receive data. When considering IoT deployments, it is necessary to evaluate various sensors and IoT devices, and how they share and receive data for future integration. Part of this evaluation entails gauging the advantages and disadvantages of individual IoT protocols, which enable communication exchange between smart devices and sensors. Although there are multiple IoT protocols, here we will compare two prominent light IoT protocols: LwM2M vs MQTT.
What is the LwM2M Protocol?
OMA Lightweight M2M (LwM2M) is a fast, light, and structured session-based protocol with an efficient resource data model. Created by the Open Mobile Alliance, LwM2M enables most IoT functionalities while maintaining Device Management capabilities on restricted devices. It is frequently used with the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP), which we will discuss in the upcoming blog series.
What is the MQTT Protocol?
The message queuing telemetry transport (MQTT) is a Client-Server publish/subscribe messaging transport protocol that supports one to many communications mediated by brokers. Clients can publish messages to a broker and receive messages by subscribing to a broker-related topic. It is a lightweight protocol that is used to exchange data between applications, middleware, and sensors. MQTT is used to enable an event-driven exchange of messages between devices, across networks. This protocol is most often used to route information between IoT devices with low memory, bandwidth, and power capacities.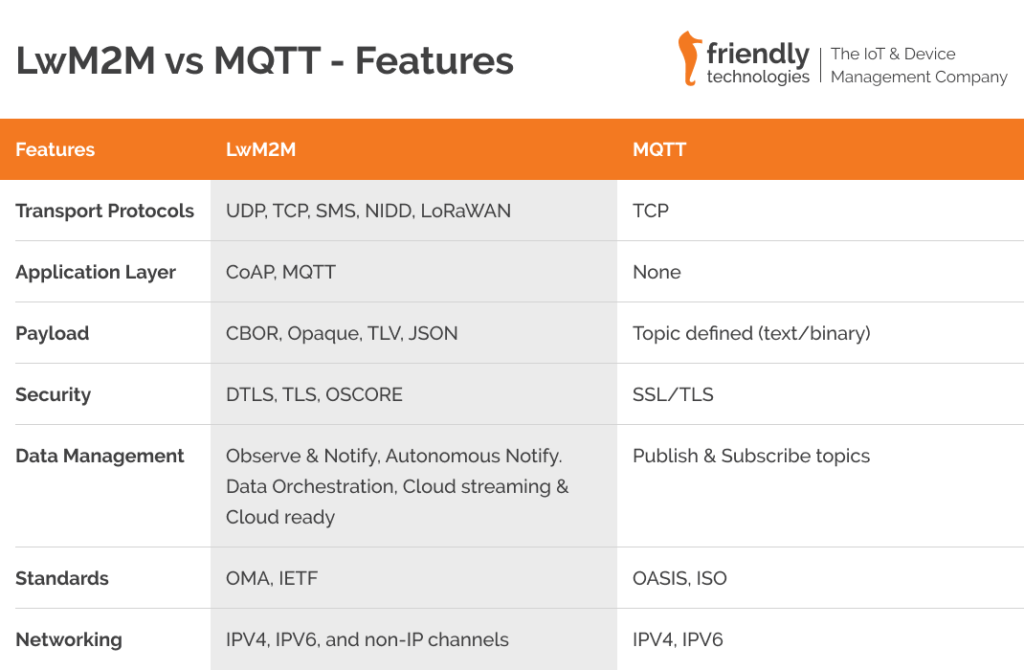
LwM2M vs MQTT – Feature Comparison
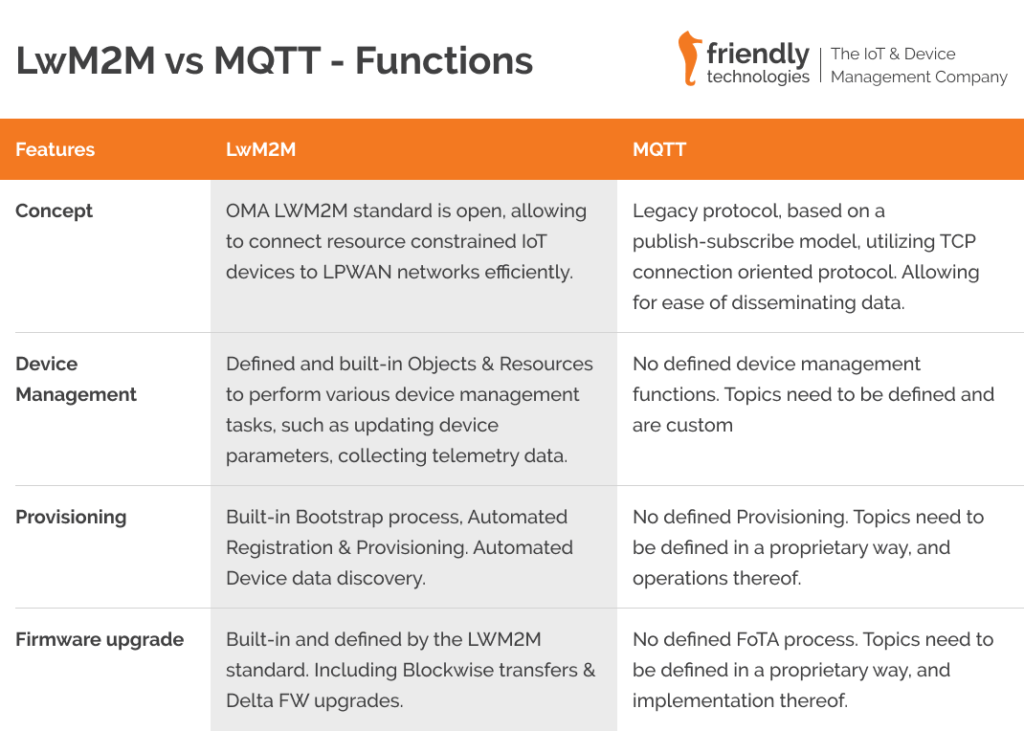
LwM2M vs MQTT – Function Comparison
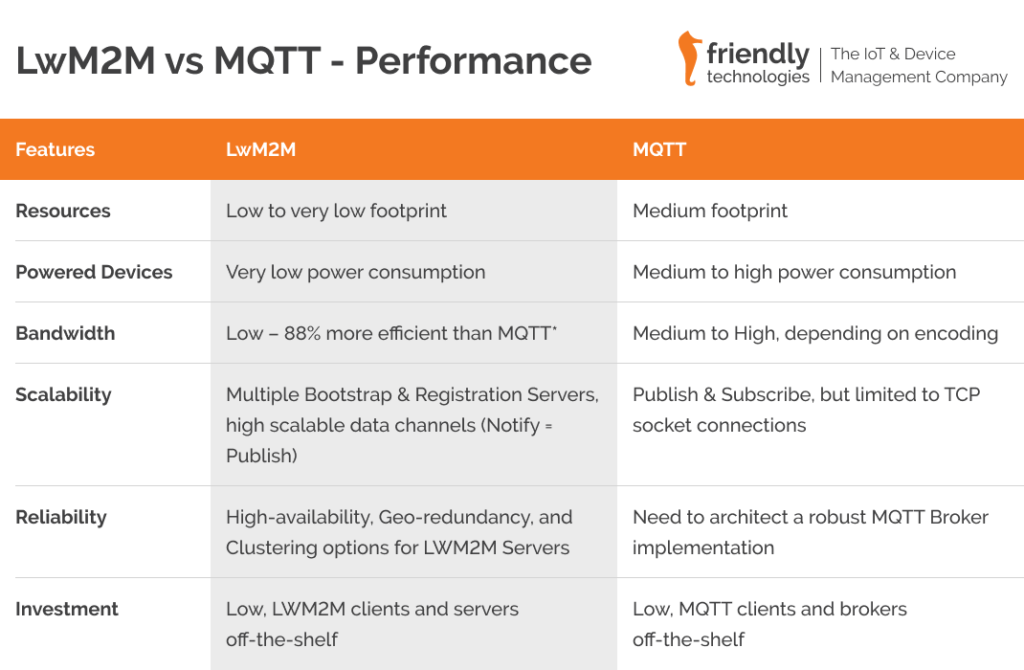
LwM2M vs MQTT – Performance Comparison
Comparing LwM2M vs MQTT: What’s Similar?
IoT systems are often plagued by proprietary vendor solutions and systems. As a result, standard protocols offer a safe haven in the midst of an increasingly chaotic IoT environment.
- Both MQTT and LwM2M are standard protocols that help exchange data between devices, systems, sensors, and applications.
- LwM2M and MQTT have thriving working groups associated with specification and further protocol development which makes this a preferred choice among a variety of IoT projects.
- Both are lightweight and easy to implement, require minimal resources, and can be used on small microcontrollers. They are suited for low-power, resource-constrained devices, gateways, and sensors operated on low-bandwidth networks.
- Both support bi-directional communication and scaling to connect millions of IoT devices.
Comparing LwM2M vs MQTT: What’s Different?
MQTT has a well-established record across industry verticals such as Automotive, Logistics, Manufacturing, Smart Home, consumer products, and transportation. It is a lightweight publish-subscribe message transfer protocol mediated by a central MQTT broker. It has been in use since first developed in 1999 and submitted by IBM to OASIS specification in 2013 making it a venerable protocol. In contrast, OMA Lightweight M2M is a protocol from Open Mobile Alliance designed for M2M and IoT device management and service enablement for telecom networks making it more suitable for accelerated IoT-related scenarios.
Here are some noteworthy differences between the two popular IoT protocols:
Differences in Purpose
The Lightweight M2M is a structured device management and service enablement protocol based on CoAP request-response and with the evolved specification versions supports a variety of message transport protocols. MQTT is a Client-Server publish/subscribe messaging transport protocol that supports data and proprietary device management payloads in IoT.
Differences in Structure
LwM2M features a straightforward data and communication model. It contains standard objects (OMNA, IPSO, GSMA Objects) and structured core functions for Connectivity monitoring, Remote device actions, Firmware update, Software Update, Lock & Wipe, Bootstrap, Diagnostics, etc. It can therefore be used for data reporting and device management. With MQTT, these features are entirely vendor and platform-specific. With LwM2M, it is necessary to conduct firmware updates or any other management features must be from scratch, and adapted to each device.
Differences in Data Processing Times
MQTT is particularly known for fast data transfer, especially when it comes to one-to-many message distribution, which allows users to take necessary steps proactively in real-time. Nevertheless, system complexity and network architecture play a role as well.
LwM2M offers a more robust architecture, while comparing favorably with MQTT in terms of response time, LwM2M minimizes the bandwidth utilizing CoAP over UDP Consequently offers better performance for constrained devices.
Transport and Binding
MQTT is designed to run over TCP/IP, MQTT-SN (Sensor Network) is designed to work over UDP, Zigbee, or other network protocols that can provide bi-directional connection, however, it has yet to be widely adopted by the industry.
LwM2M was designed to run over a variety of transport layers, including UDP, TCP, Non-IP Data delivery, SMS, CIoT & LoRaWAN, having the ability to control and trigger sleepy devices over the supported binding transports.
Interoperability
The combination of various constrained devices in IoT solutions is increasing constantly, which results in a mix of different vendors offering devices and sensors over a single IoT deployment. LwM2M Client-Server interoperability becomes a major advantage when deploying a variety of solutions in an IoT project, they can be easily integrated when both client and server support LwM2M standards, however, this integration is always a challenge when using MQTT proprietary device management payloads.
Overall Differences of LwM2M vs MQTT
MQTT is first and foremost a telemetry protocol. However, it can also be applied as a base to develop proprietary device management functionalities. LwM2M, on the other hand, has the upper hand of being an IoT device management and service enablement protocol that can also be applied in telemetry use cases.
- MQTT features a data and device management model that is clear-cut. Ideal for lightweight devices and sensor networks with low-power capacity.
- LwM2M can be used on both lightweight and resource-intensive devices, making it popular in IoT scenarios.
Comparing LwM2M vs MQTT: How about Security?
Security of data communication especially during provisioning or device management is crucial for IoT solutions.
MQTT relies on transport layer security SSL/TLS for authentication and data security it doesn’t offer any advanced protection mechanism. The support of TLS also adds an additional network overhead, which can be burdensome. As a result, business users often have to compromise on speed, functionality, and lightness in order to achieve security.
LwM2M is in direct contrast to MQTT when it comes to security. It supports OSCORE, thanks to which one can rest assured of end-to-end application-layer security. It is compliant with DTLS 1.2+ and TLS 1.2+ protocols natively, making it similar to MQTT with respect to transport-layer security. Using LwM2M credentials management mechanism one can encrypt only the payload object that will eliminate the need to encrypt all the traffic and reduce DTLS handshake overhead. It must be noted that despite tough security measures, the LwM2M protocol remains highly responsive and agile.
Security advantages of LwM2M:
- End-to-End Security using OSCORE
- DTLS protocol for strong security
- No intrinsic security issues.
- Built-in key-based authentication is supported
- Certificates are enabled natively
- Impressive security performance even in challenging environments
Which is Better: MQTT or LwM2M?
In order to determine which protocol is the best fit, one should consider the context of the use case that will best fit the process and if the protocol can be easily and efficiently integrated with the device.
Although MQTT and LwM2M protocols have a number of differences, they are both suitable for device management that is resource-constrained.
LwM2M would be ideal for constrained and low-power devices, it is also a reliable option for cellular technology applications that want to minimize the amount of transferred data. LwM2M is based on the CoAP model, designed with resource-constrained devices while adding rich device management on top of the transport layer, supporting ready-to-use standard objects, connectivity monitoring, and remote device actions (FOTA / SOTA).
MQTT which is more focused on transporting and pushing data between nodes (as device to platform) doesn’t offer the type of device management but utilizes a more proprietary approach for these features that are vendor-specific.
LwM2M is a robust protocol that is suitable for both low and high-intensity IoT projects. It is perfect for projects that may scale in the future, and that involves challenging and diverse hardware infrastructure. In addition, LwM2M ensures interoperability and eliminates vendor lock-ins. LwM2M can be deployed instantly and helps reduce time to enter the market. One will have to build device languages separately for each project when it comes to MQTT. This makes it unsuitable for complex projects.
Ready to talk about your requirements and which protocol suits your project best? Let’s chat! Contact us to learn more and request a demo.
See also:

Explore Other Topics
Friendly News
Telecom Blog
IoT Blog
Embedded Blog
Smart Home Blog
Webinars
Whitepapers

Friendly IoT Device Management
One-IoT™ Device Management
IoT Application Enablement
Friendly Smart Home
Embedded Clients
Friendly LwM2M client
Friendly OMA-DM Client
Friendly Partners
Commercial Partners
Device Manufacturers
Resources
Blog & News
Glossary
Webinars
About Friendly Technologies